Dive into a time machine with us as we set the dial back to the 1990s—an era where flannel was the fabric of choice, and the digital landscape as we know it was just taking form. From the birth of the World Wide Web to the inception of mobile phones that would eventually become our lifelines, the 1990s technology innovations laid the groundwork for the digital marketing landscape. This journey through ’90s tech will help you better understand how every HTML code and dot-com bubble played a crucial role in shaping our present-day digital-based lives.
As we peel back the layers of this transformative era, we’ll marvel at how Amazon and Google started as fledgling ventures that would revolutionize information consumption and e-commerce, or how Apple’s iMac and Wi-Fi turned concepts of design and connectivity on their heads. We’ll reminisce about the first text message sent, the buzz around the first digital cameras, and how file-sharing began to redefine music consumption with the advent of MP3 players. It’s a testament to innovation where BlackBerry’s emergence marked the beginning of the smart technologies era, setting the stage for a digital revolution that would continue to evolve well into the 21st century. So, fasten your seatbelts—we’re on a rewind to the 1990s, exploring how tech inventions shaped us and how they’re deeply embedded into the blueprint of our future!
Flashback! The Internet In 1995 | Archives | TODAY
World Wide Web
The inception of the World Wide Web (WWW) in the 1990s by Sir Tim Berners-Lee, a British computer scientist at CERN, marked a pivotal moment in digital communication and information sharing.

Tim Berners-Lee and the Birth of WWW
Growing up with a keen interest in trains and electronics, Berners-Lee’s early fascination with technology led him to Oxford University, where his journey into computer science began. At CERN, he identified the challenge scientists faced in sharing information across different computers and saw the potential of interconnected information through the emerging internet and hypertext technology. In 1989, Berners-Lee proposed a visionary solution, “Information Management: A Proposal,” which, despite initial skepticism, laid the foundation for the WWW. By 1990, he had developed HTML (HyperText Markup Language), URI (Uniform Resource Identifier), and HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol), essential technologies that underpin today’s web. Recognizing the web’s potential for universal access, Berners-Lee and CERN decided to make the web technology available on a royalty-free basis, a decision that catalyzed a global wave of creativity and innovation.
Early Browser Wars: Netscape vs. Internet Explorer
The mid-1990s witnessed the “Browser Wars,” a fierce competition between Netscape Navigator and Microsoft’s Internet Explorer. Netscape, led by Marc Andreessen, quickly rose to prominence with its user-friendly Navigator browser, capturing a significant market share. However, Microsoft entered the fray by bundling Internet Explorer with the Windows operating system, offering it free of charge. This strategic move, coupled with rapid advancements in browser features, shifted the balance. Despite Netscape’s early lead, Microsoft’s aggressive tactics and integration strategy eventually led to Internet Explorer dominating the market. These browser wars not only shaped the future of web browsing but also highlighted the importance of web accessibility.

Impact on Information Access and Communication
The launch of “WWW” revolutionized how people access information and communicate. It broke down geographical barriers, making it possible to share knowledge and connect with others worldwide instantaneously. The rise of social media platforms further transformed personal and professional interactions, enabling users to create content, engage in discussions, and form communities based on shared interests. Moreover, the web’s influence extended to the retail industry, where it dramatically changed consumer behavior and expectations, making online reviews, user-generated content, and e-commerce integral to the shopping experience.
Like This Blog? Check Out Exploring The Evolving World Of Digital Advertising: A Modern Guide
The World Wide Web’s development in the 1990s, spearheaded by Tim Berners-Lee, fundamentally altered the landscape of digital marketing. By facilitating unprecedented access to information and enabling new forms of communication, it laid the foundation for the digital marketing strategies today. From the early browser wars to the transformative impact on communication and commerce, the web’s evolution continues to shape the digital world, underscoring the enduring legacy of the innovations of the 1990s.
Mobile Phones, From ‘Brick Phones’ to Portable Communicators
The journey of mobile phones from ‘brick phones’ to sleek portable communicators marks a significant evolution in telecommunication. Initially, mobile phones like the Motorola DynaTAC 8000X, introduced in 1983, were substantial in size and primarily used for voice communication, boasting basic functionalities such as making and receiving calls. These devices, often likened to a small brick due to their heft and appearance, laid the groundwork for the smartphone revolution. The transition to more portable models during the 1990s signified a leap in mobile phone technology, with manufacturers focusing on reducing size and weight, thus making them more accessible to a wider audience. This era witnessed rapid innovation, introducing features beyond basic voice communication, such as the Short Message Service (SMS), which revolutionized communication by offering a less intrusive way to convey topics.
The Nokia 1011 and Text Messaging
The Nokia 1011, launched on 10 November 1992, is widely regarded as the first mass-market GSM (2G) phone. This model was a significant departure from its analog predecessors, featuring a distinctive diamond-shaped earpiece and engineered to accommodate an extendable antenna within a groove of the removable battery. However, the antenna became a source of controversy, as partially extending it could degrade call quality significantly. The Nokia 1011’s introduction to the market was a landmark event, being the first mass-produced phone to utilize the GSM digital mobile networks. This standardization allowed users to enjoy seamless mobile communication across Europe without the need to change handsets, a feature underpinned by the introduction of the Subscriber Identity Module, or SIM card.
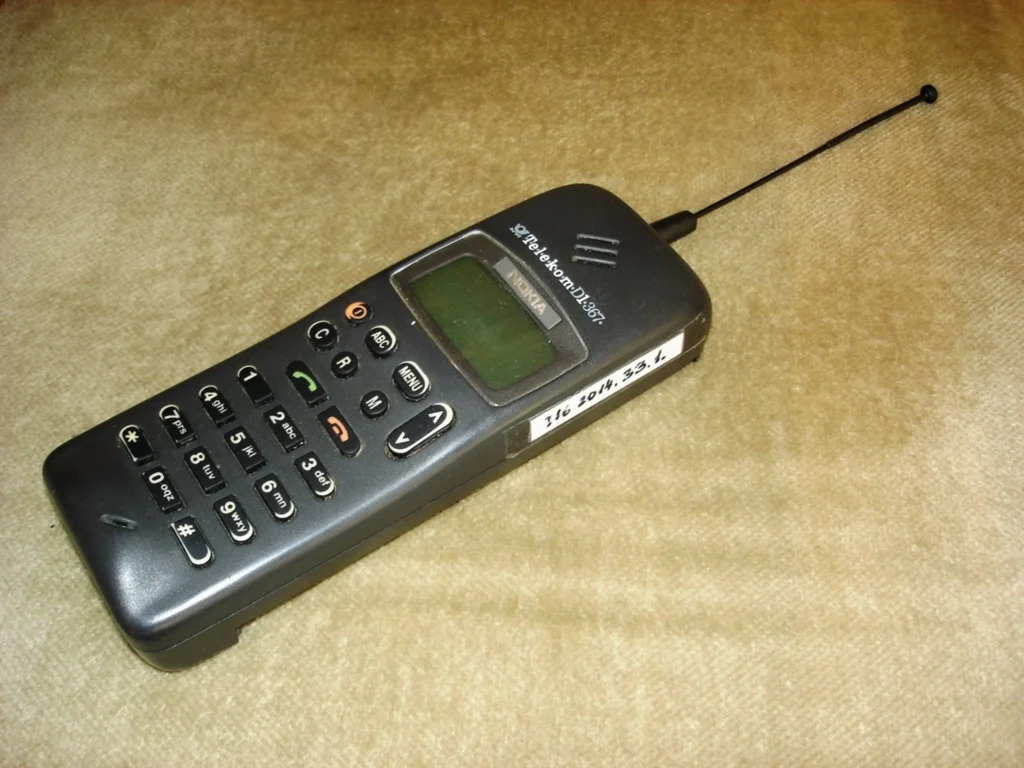

Mobile Phones in Fashion: The Nokia 3210
The Nokia 3210, launched in 1999, represented a paradigm shift in mobile phone culture. It was one of the first phones to feature an internal antenna and came preloaded with games like Snake, marking the beginning of mobile gaming. Its design, characterized by customizable ‘Xpress-On’ covers, allowed users to personalize their devices, reflecting a move towards more individualistic and expressive consumer electronics.
The Nokia 3210’s Design
The 3210’s design embodied a new organizational style, emphasizing flexibility and products that mirrored this ethos. This model became a nostalgic icon, with companies like Lekki refurbishing old 3210s, highlighting the enduring appeal of its design and the significant role it played in the evolution of mobile phones as personal and customizable devices. The 3210’s success, selling 160 million units, underscores its impact as one of the most popular and influential phones in history, setting a precedent for the future of mobile communication.
The evolution of mobile phones in the 1990s, from the first mass-market GSM phone to the iconic Nokia 3210, showcases a period of rapid technological advancement. The ability to personalize devices and engage in mobile gaming introduced new ways for brands to connect with audiences, highlighting a significant impact of ’90s technology.
The Rise of Personal Computers
Windows 95 was a game-changer in the world of personal computing. Launched amidst excitement and anticipation, Windows 95 introduced a host of features that altered the way users interacted with their PCs.

At its core, the introduction of the Start button and menu revolutionized the desktop interface, providing a single point of access for applications, settings, and system functions. This ease of navigation, combined with features like the taskbar for managing running applications and the system tray for quick access to essential utilities, marked a significant leap forward in user interface design.
Moreover, Windows 95 was pivotal in making personal computers more user-friendly and accessible to a broader audience. Its support for Plug and Play (PnP) technology simplified hardware installation, allowing for automatic recognition and configuration of new components. The operating system also came with built-in Internet capabilities, including a TCP/IP stack and the debut of Internet Explorer, highlighting Microsoft’s early focus on the importance of digital networking.
Growth in Home PC Usage
The 1990s witnessed an unprecedented surge in home PC ownership, a trend significantly influenced by the advancements in personal computing, spearheaded by operating systems like Windows 95. Between 1990 and 1997, the percentage of households owning computers jumped from 15 percent to 35 percent. This era of rapid technological development saw people becoming increasingly comfortable with graphical user interfaces, multimedia CD-ROMs, and the Internet, which in turn fueled greater computer ownership. As understanding and accessibility of computers increased, so did the average household expenditure on computers and associated hardware, more than tripling during this period.
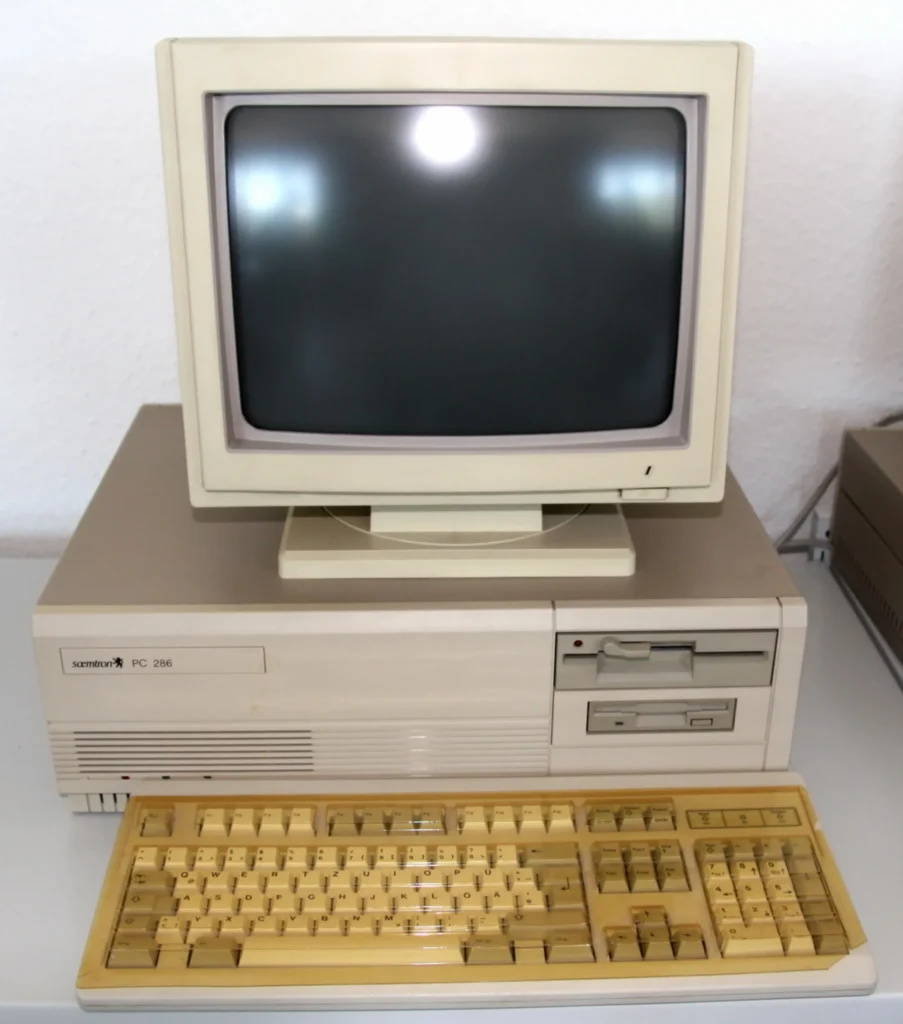

PCs Driving Digital Transformation
The evolution of personal computers in the 1990s was not just about hardware and software advancements, but also about their role in driving digital transformation across industries. IT professionals, leveraging technologies like AI and cloud computing, were at the forefront of this shift, implementing solutions that revolutionized industries by enhancing efficiency and streamlining processes. The expansion of digital ecosystems lead to robust cybersecurity measures, further emphasizing the critical role of PCs in safeguarding sensitive data and protecting organizations from cyber threats.

Early Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Artificial Intelligence (AI) became a buzzword in the tech industry, playing a significant role in digital transformation. AI technologies such as machine learning and natural language processing automated tasks, analyzed vast amounts of data, and provided valuable insights, thereby transforming business operations across various sectors. From chatbots in customer service to predictive analytics in supply chain, AI, powered by advanced PCs, reshaped the way businesses operate and interact with their customers.
The Growth of IT Professionals
The demand for IT professionals skilled in navigating the digital landscape has surged, underscoring the importance of personal computers in the digital age. This era offers diverse career opportunities, ranging from software development and data analysis to cybersecurity and cloud management, all rooted in the foundational advancements of personal computing technology in the 1990s.

The 1990s were a pivotal decade for personal computers, marking milestones such as the launch of Windows 95, a dramatic increase in home PC usage, and the pivotal role of PCs in driving digital transformation. These developments laid the groundwork for the digital marketing strategies and technological landscape that companies are competitively using today, highlighting the lasting legacy of ’90s tech innovations.
MP3 Players
The MP3 format, introduced as an audio coding standard in 1994, represented a significant leap in the way audio data could be compressed and shared. It utilized advanced compression techniques such as the modified discrete cosine transform (MDCT), FFT, and psychoacoustic methods, allowing for high-quality audio files to be significantly reduced in size without losing much quality. This breakthrough was led by a team of engineers, including Karlheinz Brandenburg, who is often referred to as the “father of the MP3”. Their work made it possible to compress audio files to a fraction of their original size, paving the way for a new era of digital music consumption.
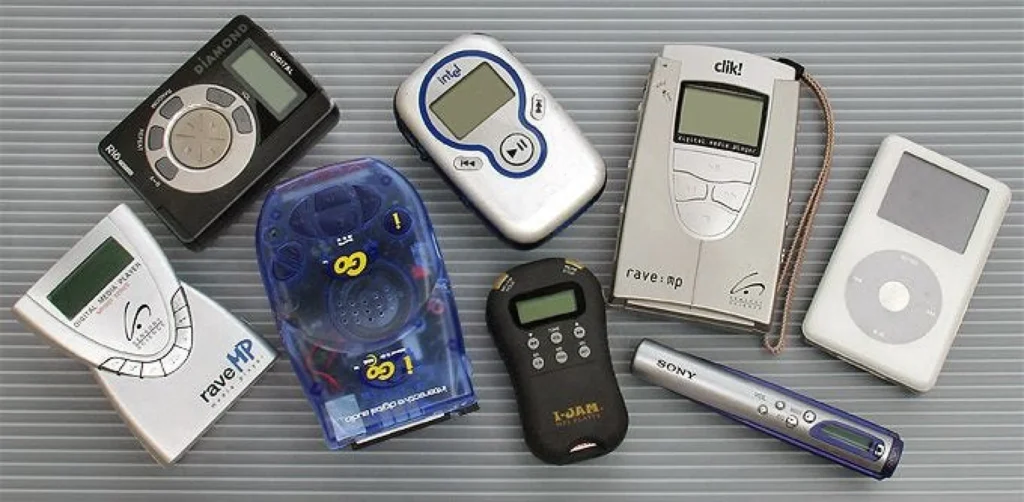
First Portable MP3 Players
The first portable MP3 player was launched in 1997 by SaeHan Information Systems, marking a new chapter in the world of audio devices. This device, the MPMan F10, was initially sold in South Korea in 1998 before being licensed for North American distribution to Eiger Labs, who rebranded it as the EigerMan F10 and F20. These had storage capacities of 32 MB or 64 MB and could hold 6 or 12 songs and featured an LCD screen to display the song currently playing. Shortly after, the Rio PMP300 by Diamond Multimedia was introduced, featuring a similar storage capacity and becoming a hit during the holiday season. Despite legal challenges from the RIAA, MP3 players were ruled legal, with the Rio PMP300 gaining notoriety as the target of a major lawsuit.
Influence on Music Consumption
The emergence of MP3 players revolutionized music consumption by making it more accessible than ever before. This portability transformed how people listened and interacted with music, leading to a shift from traditional CD formats to digital formats.
Welcome To Napster
The ability to carry hundreds of songs in a compact device was appealing to music lovers worldwide, marking a departure from the limitations of physical media. The widespread adoption of MP3 technology also spurred the development of file-sharing networks, most notably Napster, which changed listening patterns by allowing users to access vast collections of music online. This led to a new relationship between digital information and ownership, challenging traditional market models based on scarcity.

The MP3’s journey from an inferior product compared to CDs to becoming the preferred choice for the majority highlights the impact of technological advancements on consumer preferences. Despite initial resistance due to lower audio quality, the MP3 format’s convenience, smaller data footprint, and the rapid development of its ecosystem made it a better option than CDs for most people.
Do You Remember When Metallica Sued Napster?
Founding of Google by Larry Page and Sergey Brin
The inception of Google traces back to 1996, born from the intellectual synergy between Larry Page and Sergey Brin, two Stanford students with a shared vision yet differing perspectives. Initially, their project, known as “BackRub,” leveraged the concept of citations across the web to rank pages, a novel approach that distinguished it from other search engines primarily focused on keyword matching. Their dorm rooms became the cradle of innovation, where they pieced together a computational Frankenstein to bring their vision to life. By August 1996, Google made its debut on the Stanford website, quickly gaining traction among a niche audience. The duo’s relentless pursuit of a more organized web led to the official birth of Google Inc. in September 1998, following a pivotal $100,000 investment from Sun co-founder Andy Bechtolsheim.
Larry Page and Sergey Brin interview on Starting Google (2000)
Revolutionizing Internet Search
Google’s journey from a Stanford project to the dominant force in internet search was fueled by its innovative architecture and algorithms. Drawing inspiration from the book “Managing Gigabytes,” Page and Brin designed a search engine that not only prioritized speed and accessibility but also introduced a revolutionary way of sorting documents by relevance. The essence of Google’s success lay in its PageRank algorithm, which evaluated the importance of a page based on the web’s intricate link structure, thus delivering results that resonated with users’ queries with unprecedented accuracy. This approach propelled Google beyond its competitors, securing its position as the most popular search engine with a staggering market share.

Impact on Information Accessibility
Google’s impact extends far beyond the realm of search, touching the lives of people across the globe by enhancing information accessibility. The company’s commitment to making the world’s information universally accessible and useful is evident through initiatives like the Google Impact Challenge: Disabilities, which aims to harness technology to increase independence for people with disabilities. Through its UX research and design thinking, Google strives to create products that are inclusive, considering the needs of all users. Notably, Google has made significant strides in improving the lives of those who are blind or visually impaired, from awarding grants for accessibility tools to integrating screen readers in its products, thereby democratizing access to information.
The Introduction of DVDs
The digital versatile disc (DVD) represented a significant leap forward in home entertainment technology, offering numerous advantages over its predecessor, the VHS tape. By 2002, DVDs had surpassed VHS tapes in sales, marking a shift in consumer preference that VHS could never recover from. DVDs were more compact, provided clearer picture quality, and eliminated the need for rewinding, making them a more convenient and superior choice for viewers. Additionally, DVDs and Blu-rays were known for their durability, with the potential to last up to 20 plus years if properly cared for, unlike VHS tapes which degraded with each play.

The Rise of Home Entertainment
The introduction of DVDs in the late 1990s brought a new era of higher video quality and interactive features, swiftly overtaking videotape as the go-to format for home entertainment. By 2005, DVD sales had peaked at $16 billion, highlighting their dominance in the market. This transition from VHS to DVDs was part of a broader movement that saw physical media become a lucrative revenue stream for movie studios, allowing them to sell the same film multiple times to the same consumer across different formats. The DVD era also ushered in the concept of “binge-watching,” thanks to the ability to package entire TV series into one convenient set, fundamentally changing how audiences consumed television.
Mass Production and Market Dominance
The manufacturing of DVDs developed into a considerable industrial branch, with around 25–30 billion discs manufactured worldwide by 2004. This period saw the DVD-ROM strongly ramping up, overtaking CD-ROM production, which had peaked around 2001. The success of DVDs was not just a matter of technological superiority; it was also due to the vision of industry leaders like Warren Lieberfarb of Warner Home Video. Lieberfarb is credited with advocating for the development of a video disc format in the late 1980s, which would eventually become the DVD. His vision was to transform consumers from renters to buyers, significantly increasing profits for studios.

By the time DVDs were introduced to the U.S. market in March 1997, they were hailed as the most successful consumer electronics product launch in history, setting the stage for the digital revolution in home entertainment.
Digital Cameras and PDAs
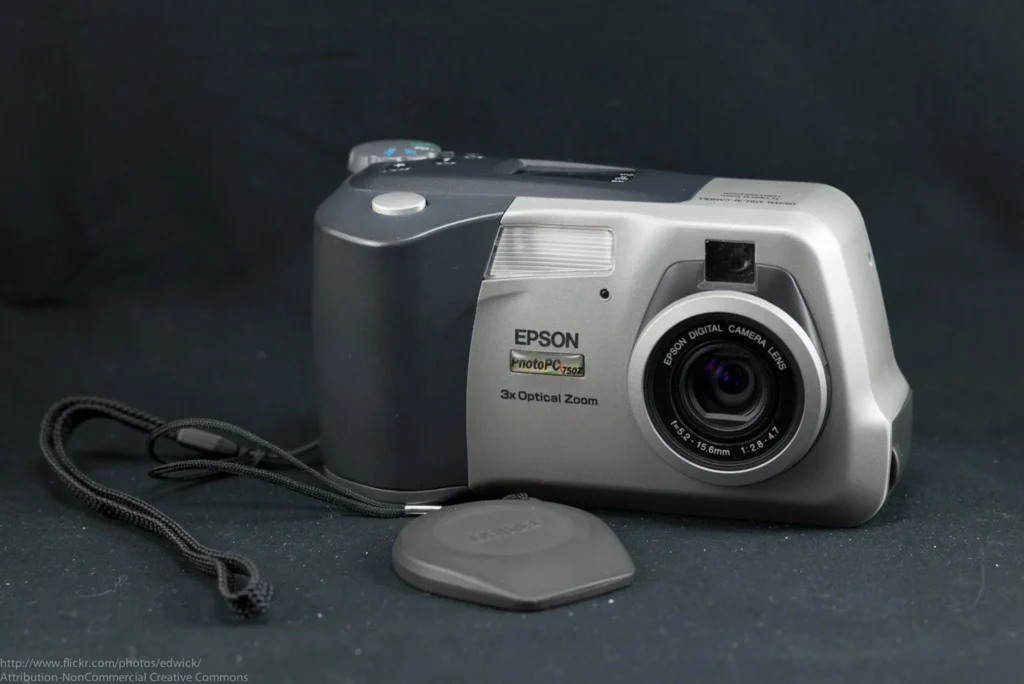
The 1990s heralded the biggest photographic revolution with the commercial introduction of digital cameras, making photography accessible to everyone. This era saw a swift transition from analog to digital, with camera manufacturers overhauling their production lines. The introduction of image sensors and memory cards replaced physical film, allowing for unlimited picture taking and storing. LCD screens on digital cameras provided instant visual feedback, revolutionizing the way photography was approached. The affordability and user-friendliness of digital cameras democratized photography, enabling anyone with a creative spark and a modest budget to explore their photographic talents. The ease of making mistakes and learning from them transformed photography into a more inclusive and accessible art form.

The Palm Pilot and Personal Digital Assistants
The Personal Digital Assistant (PDA), epitomized by the Palm Pilot, emerged as a compact and portable handheld computer, offering functionalities far beyond a calculator. With the capacity to store information akin to a Personal Computer (PC), PDAs featured an address book, schedule, calendar, notepad, and email capabilities. Their convenience for quick data management in clinical and field situations, coupled with the ability to synchronize information with a PC, underscored their utility. Through wireless networks, PDAs facilitated the exchange of information anytime and anywhere, providing immediate access to essential clinical and administrative data. Despite facing barriers such as insufficient security and technical support, PDAs were widely adopted in healthcare practice, with their usage expected to increase.
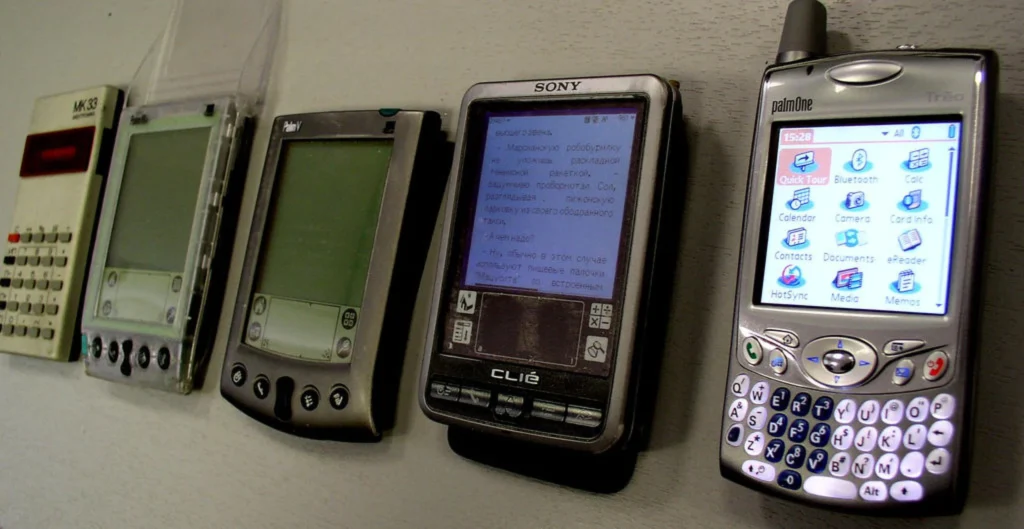

Palm, Inc., a California-based company, developed the Palm line of PDAs and mobile phones, becoming synonymous with the early handheld computing era and paving the way for the smartphone era. The first Palm device, the PalmPilot 1000, released in 1996, marked a significant milestone in portable computing devices. Palm’s devices, running on the in-house Palm OS and later Windows Mobile, continued to evolve, merging with smartphones to offer comprehensive functionalities including mobile phone, email, MMS, and instant messaging (SMS) technologies. This evolution highlighted the shift towards integrating multiple functionalities into a single device, significantly impacting personal and professional communication.
Technological Convergence and Impact on Daily Lives
The innovation of digital communication in the 1940s laid the groundwork for media convergence. The internet has become the epicenter of convergence, serving as a hub where various forms of media content are created, distributed, and presented. The creation of notebook computers, smartphones, and tablets has accelerated the pace of media convergence, making the concept of accessing any media content, anywhere, a reality. The merging of media onto single devices like tablets or smartphones has blurred the distinctions between previously separate media formats. This convergence has also facilitated multitasking, allowing users to engage with multiple forms of media simultaneously, further altering our relationship with the internet.

Mobile devices and social media have transformed our internet experience. The shift towards smaller screens and the prevalence of apps have introduced a more managed form of the internet, contrasting with the open internet facilitated by search engines like Google. This evolution reflects a broader trend of technological convergence reshaping daily lives and communication practices.
Conclusion: Why We Love The 90’s So Much
The 1990s were a decade of groundbreaking advancements that transformed the digital marketing industry. As we look to the future, it’s evident that the legacy of 1990s technology will continue to influence the development of all things digital in our futures.
FAQs
How Did the 1990s Change the Technological Landscape?
The 1990s were a transformative period for technology, primarily through the widespread adoption of the Internet and World Wide Web, which connected homes and offices globally. This era saw the emergence of dominant tech companies, often referred to as “gorillas,” that developed increasingly sophisticated systems. Simultaneously, nimble startups leveraged the internet to innovate and disrupt, leading to a surge in their share prices.
What Innovations Are Transforming the World Today?
Today’s world is being reshaped by the advent of social media, video conferencing, and instant messaging, which have made communication instant and without borders. This new level of interconnectedness has drastically changed personal interactions, business operations, and the nature of global collaboration.
What Were the Key Technological Breakthroughs of the 1990s?
The 1990s were rich in technological innovations that laid the groundwork for many of today’s gadgets and digital platforms. Some of the most notable advancements include the development of smartphones, digital cameras, targeted Internet searches, and the World Wide Web. This era also saw the birth of emojis, and the foundations for platforms like Snapchat and Instagram were laid.
Why Was the Tech Boom of the 1990s Significant?
The tech boom of the 1990s was a pivotal period that marked the beginning of the Information Age. During this decade, the percentage of U.S. households with computers jumped from 15% to 35%, signaling a shift from viewing computers as luxury items to essential tools. This boom led to the establishment of numerous technology-based companies and fundamentally changed the economic landscape to focus on information technology.








